U.S. maternal mortality rates are alarmingly high, making the United States one of the leading high-income countries for pregnancy-related deaths. Recent studies show that over 80% of these pregnancy-related fatalities could potentially be prevented, highlighting significant gaps in maternal health care. Factors contributing to this distressing trend include inadequate prenatal and postpartum care, along with stark maternal health disparities across racial and ethnic groups. With a reported 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022, many are calling for urgent action to address these preventable maternal deaths. This critical issue demands our attention as it impacts families and communities nationwide.
The challenges surrounding pregnancy-related fatalities in America reflect deep-rooted issues in maternal health care systems. Examining preventable pregnancy-associated deaths reveals the need for improved policies and practices in maternal safety. Many women, particularly those from marginalized communities, face systemic barriers that exacerbate their risk during and after childbirth. The disparities in maternal health outcomes underscore the importance of comprehensive postpartum care and access to adequate healthcare services. Overall, addressing these complex issues is vital to enhance maternal health and reduce the detrimental impacts of high maternal mortality rates.
Understanding U.S. Maternal Mortality Trends
The alarming rise in maternal mortality rates in the United States has raised significant concerns among health professionals and policymakers. As reported in recent studies, the U.S. leads high-income countries in maternal mortality, with rates continuing to climb each year. Notably, the prevalence of pregnancy-related deaths, particularly those that are preventable, underscores a critical crisis in maternal health care. According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, over 80% of these deaths could have been avoided, indicating profound flaws in the healthcare system, especially regarding access and quality of care for expecting mothers.
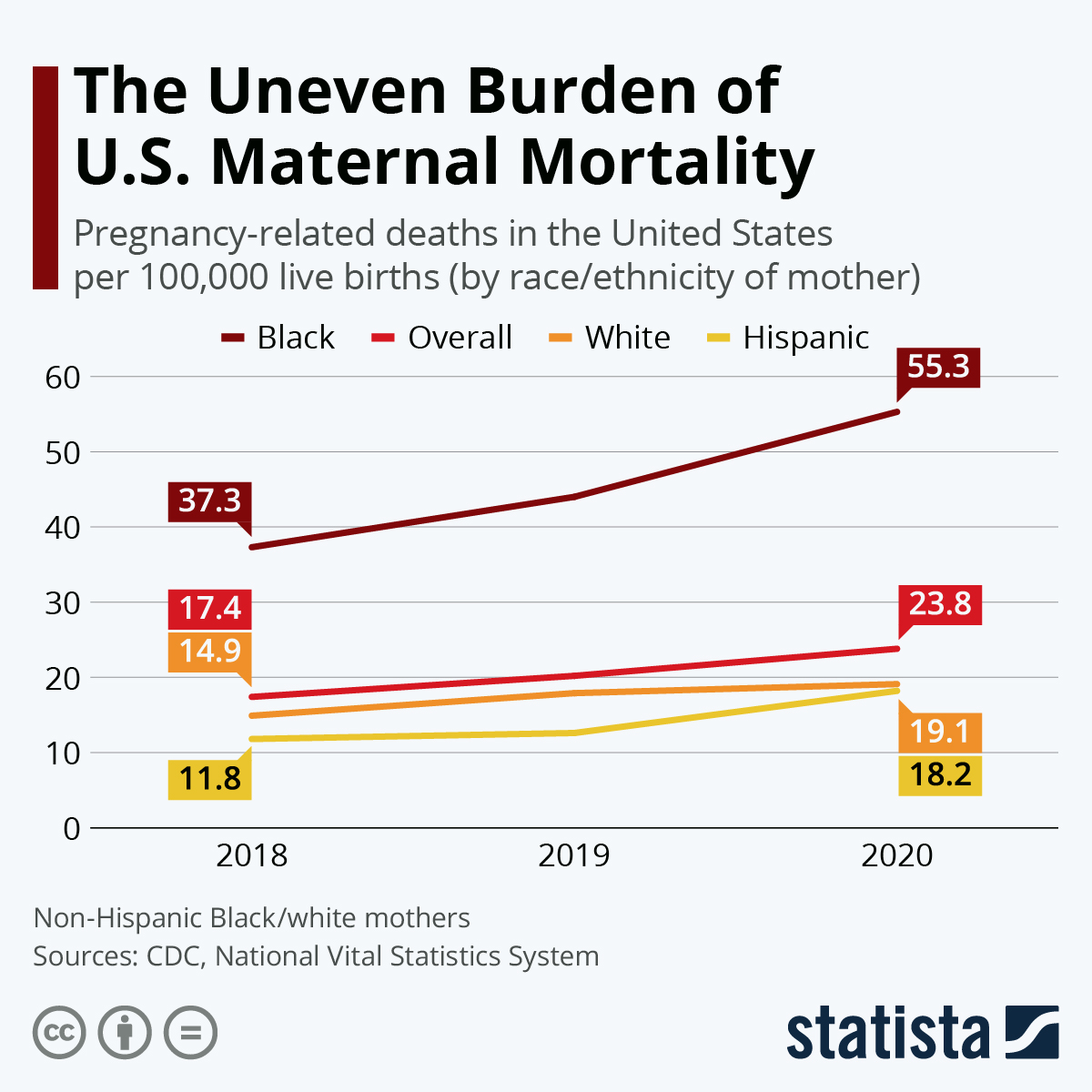
Racial and ethnic disparities further complicate the issue of maternal mortality, emphasizing the urgent need for targeted interventions. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience nearly four times the mortality rate of white women, showcasing an immense gap that reflects broader societal inequities. The need for comprehensive studies and effective public health initiatives focusing on these disparities is crucial. By understanding the underlying factors contributing to this high maternal mortality rate, stakeholders can work towards creating equitable health care solutions that address the needs of all populations.
Factors Contributing to High Maternal Mortality
Multiple factors contribute to the rising rates of maternal mortality in the U.S., making the issue complex and multifaceted. A primary concern is the fragmented healthcare system, which may lead to inadequate prenatal care and postpartum support. Maternity care deserts—geographic areas where access to maternal health care services is limited—worsen the situation, especially in rural communities. Moreover, systemic biases and discrimination paint a troubling picture of maternal health disparities among different racial and ethnic groups, highlighting the necessity for a more integrated approach to maternal health care.
Chronic health conditions, such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease, increasingly affect younger reproductive-age individuals, complicating pregnancy outcomes. The shift from hemorrhage to cardiovascular complications as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths speaks volumes about the transformation of health challenges faced by expectant mothers. Addressing these chronic conditions through early intervention and comprehensive prenatal care can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the high rate of preventable maternal deaths.
The Importance of Extended Postpartum Care
Postpartum care is a crucial but often overlooked aspect of maternal health care, yet it plays a significant role in reducing maternal mortality. Recent studies delineate that late maternal deaths—occurring between 42 days and one year after childbirth—account for a substantial proportion of pregnancy-related fatalities in the U.S. This finding suggests that rather than viewing postpartum care as a six- to twelve-week period following birth, health systems must adopt a continuum approach to maternal health that encompasses the challenges new mothers face in the months and year following delivery.
Improved extended postpartum care can lead to better tracking of maternal health issues and provide the necessary support for conditions that may arise post-delivery. This could involve interventions like regular follow-ups for chronic health conditions, mental health support, and education regarding postpartum recovery. By prioritizing continuous care and addressing the disparities in health outcomes, the U.S. can work towards reducing the disturbing rates of maternal mortality and ensuring that mothers have the resources they need to thrive.
Reducing Preventable Maternal Deaths in the U.S.
Preventable maternal deaths present a significant challenge to the U.S. healthcare system, with the data indicating that many of these fatalities are entirely avoidable. Implementing quality care protocols during pregnancy and enhancing postpartum support can lead to a substantial decrease in these preventable complications. Efforts to standardize care practices across different states and to ensure that healthcare providers are adequately equipped to handle varying needs for maternal health can greatly benefit women at risk.
Moreover, raising awareness and knowledge about maternal health disparities is essential for driving policy changes. Invested stakeholders—including healthcare providers, policymakers, and community leaders—must collaborate to identify the barriers to care that exist, especially in underserved areas. With focused efforts to enhance public health funding and initiatives aimed At correcting systemic injustices, the U.S. can aspire to reduce its maternal mortality rates significantly and eradicate preventable deaths related to pregnancy.
The Role of Policy in Maternal Health Disparities
Policy plays a critical role in shaping maternal health outcomes across the United States. Despite the existence of innovative solutions and a growing recognition of the critical need for equitable maternal care, significant differences in how states approach maternal health persist. Policymaking that fails to consider the socioeconomic and racial factors affecting women ultimately contributes to the broad disparities observed in maternal mortality rates, warranting focused reforms and comprehensive health policy changes.
Engaging in evidence-based policymaking can lead to progressive reforms aimed at closing health gaps. State-level initiatives should be inclusive of voices from diverse communities and incorporate data-driven strategies that address the unique needs of different populations. Only through comprehensive policy efforts can the U.S. hope to see not only a reduction in maternal mortality rates but also systemic improvements that ensure equitable and high-quality maternal health services for all women.
Innovative Solutions for Maternal Health
Innovation in maternal health care is essential to combatting the rising trend of maternal mortality in the U.S. As healthcare providers and researchers seek effective solutions, the integration of technology, data analytics, and supportive community programs can yield significant improvements. For instance, telemedicine has emerged as a vital resource, enabling better access to specialists and postpartum care for women living in isolated or underserved communities. Embracing such innovations can help bridge the gaps in care and bolster maternal health outcomes across various demographics.
Moreover, fostering collaboration among various health stakeholders—including healthcare systems, community organizations, and policymakers—can drive meaningful change. The establishment of supportive networks that focus on women’s health equity and access to care can facilitate a holistic approach to maternal health. By investing in innovative solutions, we can provide better care not just during pregnancy but throughout the entire maternal health continuum, significantly reducing preventable maternal deaths.
The Importance of Comprehensive Maternal Data Collection
A robust and comprehensive maternal health data collection system is fundamental to understanding and addressing maternal mortality issues in the United States. The lack of consistent, nationwide tracking of maternal deaths until recently has hindered efforts to develop targeted interventions and meaningful policy changes. Now that improved systems are in place to capture maternal health data, it is crucial to ensure that the information collected is analyzed effectively to inform practices that can save lives.
A thorough analysis of maternal health data can shine a light on existing disparities and issues that require urgent attention. By leveraging this data, healthcare providers and policymakers can develop tailored programs and initiatives aimed at reducing maternal mortality rates, particularly in vulnerable populations. Continuous monitoring and a commitment to adapting strategies based on data insights will be essential moving forward to promote better maternal health outcomes across the nation.
Addressing Racial Disparities in Maternal Health
Addressing the stark racial disparities in maternal health outcomes is a critical step in tackling the national issue of maternal mortality. The data indicates that American Indian and Alaska Native women experience the highest rates of pregnancy-related deaths, followed closely by non-Hispanic Black women, revealing systemic inequalities that must be addressed. Initiatives focused on culturally competent care and community-led health interventions are essential for closing these gaps and improving healthcare access for marginalized groups.
Moreover, educational programs aimed at healthcare providers about implicit bias and the unique challenges faced by women of color can help foster more equitable care environments. By empowering community organizations and engaging directly with affected populations, stakeholders can promote better awareness and advocacy for maternal health issues that disproportionately impact specific racial groups. Together with systemic reforms in healthcare systems, addressing these disparities can play a pivotal role in reducing maternal mortality rates across the country.
Future Directions for Maternal Health Initiatives
Looking forward, addressing maternal health outcomes in the U.S. requires a multi-faceted approach that combines research, innovation, and targeted policy initiatives. The urgency of reducing maternal mortality rates necessitates sustained efforts in funding public health initiatives and educational campaigns aimed at improving maternal health care quality. Investing in preventative measures and community-based resources will not only benefit mothers but also their families and overall societal health.
Furthermore, collaboration between state and federal governments with healthcare entities can enhance the effectiveness of maternal health programs. Consistency in implementing best practices across states is vital for achieving nationwide improvements in maternal health outcomes. By sharing successful strategies and data-driven insights, stakeholders can work together toward a common goal: a substantial reduction in maternal mortality and the establishment of a health care system that prioritizes the needs of all mothers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are primarily cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension and stroke. This shift from hemorrhage to cardiovascular issues highlights the rising prevalence of chronic conditions among reproductive-age individuals.
Why does the U.S. have a high maternal mortality rate compared to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries due to factors such as an inequitable healthcare system, variability in state policies, maternity care deserts, and systemic bias affecting racial and ethnic groups.
How do maternal health disparities affect pregnancy-related deaths?
Maternal health disparities greatly affect pregnancy-related deaths, as seen in the significantly higher mortality rates among American Indian, Alaska Native, and Black women compared to their white counterparts. Addressing these disparities is crucial for reducing overall mortality rates.
What percentage of pregnancy-related deaths are considered preventable in the U.S.?
In the U.S., more than 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths are deemed preventable. This statistic emphasizes the need for improved healthcare practices and policies aimed at enhancing maternal health outcomes.
What role does postpartum care play in reducing maternal mortality rates?
Postpartum care is vital in reducing maternal mortality rates, particularly as nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur after the initial six weeks postpartum. Comprehensive care extending beyond this period is essential for addressing ongoing health issues.
What is the significance of late maternal deaths in the context of U.S. maternal mortality?
Late maternal deaths, occurring beyond 42 days to one year postpartum, are crucial to consider because they account for a significant portion of maternal mortality. Recognizing this period as part of maternal health care can lead to better support and interventions.
How can the U.S. improve maternal health outcomes to lower maternal mortality rates?
To improve maternal health outcomes, the U.S. needs to invest in public health infrastructure, implement innovative care solutions, and address policy discrepancies between states to ensure equitable access to quality pregnancy care.
What disparities exist in maternal mortality rates by race in the U.S.?
There are significant racial disparities in U.S. maternal mortality rates, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing the highest rates, followed by Black women, who face almost three times the mortality rate of white women.
Why is there a need for a national system to track pregnancy-related deaths?
A national system to track pregnancy-related deaths is important for understanding and addressing maternal mortality. Consistent data collection since 2018 helps identify patterns and inform policy changes aimed at preventing these tragedies.
How did the COVID-19 pandemic impact maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a sharp increase in maternal mortality rates, particularly in 2021. Research indicates that systemic health issues exacerbated by the pandemic contributed to heightened pregnancy-related deaths during this period.
| Key Points |
|---|
| More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, which continues to rise. |
| From 2018 to 2022, the mortality rate increased from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births. |
| Racial and ethnic disparities are significant; American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest rates. |
| COVID-19 pandemic likely impacted mortality rates, especially in 2021. |
| Cardiovascular disease has now become the leading cause of pregnancy-related death in the U.S. |
| Late maternal deaths (42 days to 1 year postpartum) account for nearly a third of maternal mortality. |
| Improvement in maternal health outcomes requires investment in public health infrastructure and policy changes. |
Summary
U.S. maternal mortality has reached alarming levels, with a record high among high-income countries over recent years. This issue remains profoundly concerning, as the majority of these deaths are preventable. Racial disparities continue to affect vulnerable populations disproportionately, and with over 20% of fatalities linked to cardiovascular disease, improving maternal healthcare systems is imperative. To effectively combat these statistics, comprehensive measures emphasizing better prenatal care and addressing postpartum services are crucial.