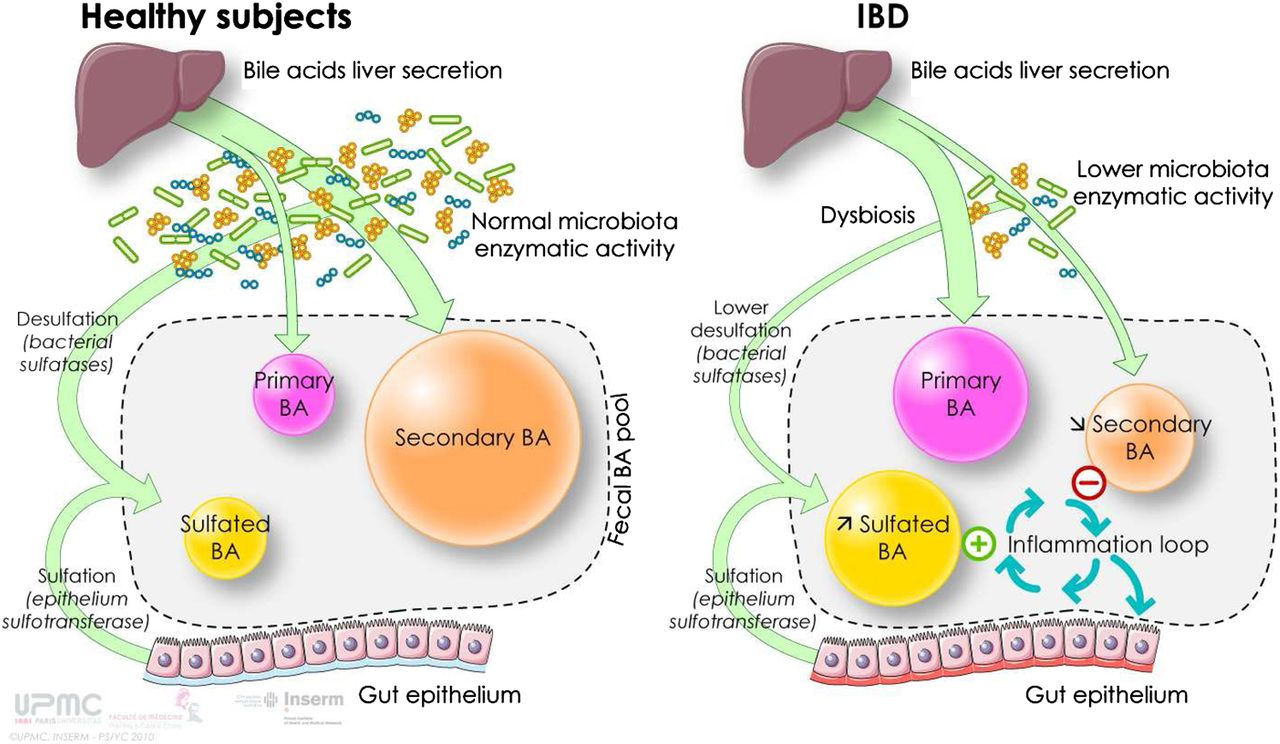
Bile acid imbalance represents a serious health concern that can significantly impact liver function and increase the risk of liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). These essential compounds, produced by the liver, are crucial not only for digestion but also for regulating various metabolic processes through bile acid metabolism. Recent research has unveiled a key molecular switch that affects bile acid regulation, contributing to the onset of liver diseases such as HCC. Furthermore, the YAP FXR signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in regulating bile production, where an imbalance can lead to inflammation and liver damage. Understanding the implications of bile acid imbalance is critical for developing effective liver disease treatment strategies and advancing our knowledge of cancer mechanisms.
The disruption of bile acid levels in the body, often referred to as bile acid dysregulation, can lead to a variety of hepatic disorders, including the aggressive hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids, fundamental substances synthesized by the liver, serve essential roles beyond mere fat digestion, acting similarly to hormones that influence metabolic health. New discoveries surrounding the intricate pathways, especially involving YAP FXR signaling, highlight how these bile acids can become problematic when their homeostasis is disturbed. As researchers delve deeper into this complex interplay, the potential for innovative treatments targeting liver diseases, including liver cancer, becomes increasingly apparent. This evolving field underscores the importance of maintaining bile acid equilibrium for optimal liver health.
Understanding Bile Acid Imbalance and Its Link to Liver Cancer
Bile acid imbalance is emerging as a significant risk factor for liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids, which are produced by the liver, not only assist in fat digestion but also play crucial roles in metabolic regulation. The recent study by Yingzi Yang highlights how the dysregulation of bile acids can initiate a cascade of events leading to liver injury and inflammation, ultimately culminating in liver cancer. This connection underscores the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis for liver health.
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway, which regulates cell growth and organ size, has been linked to bile acid metabolism disruptions. By inhibiting the FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), the YAP protein alters bile acid production, leading to an excess that can cause fibrosis and damage to liver tissue. Understanding these mechanisms paves the way for developing new liver disease treatments that target these molecular pathways, providing hope for better outcomes for patients at risk of liver cancer.
The Role of YAP and FXR Signaling in Bile Acid Metabolism
YAP protein’s pivotal role in regulating bile acid metabolism presents a fascinating insight into liver pathology. YAP can act as a repressor of the FXR receptor, which is critical for bile acid balance. When YAP is activated, it interferes with FXR function, leading to an accumulation of bile acids that can cause inflammation and fibrosis in the liver, ultimately resulting in hepatocellular carcinoma. This discovery illustrates the interplay between cell signaling pathways and metabolic processes.
Modulating the activity of YAP and enhancing FXR function may offer new therapeutic strategies for managing bile acid-related liver diseases. Options such as pharmacological agents that activate FXR or promote bile acid excretion are being explored in research. The ability to manipulate these pathways could represent a turning point in liver disease treatment, aiming not only to alleviate symptoms but also to address the underlying causes of liver cancer.
Innovative Treatment Interventions for Liver Cancer
Recent studies indicate that targeting the signaling mechanisms that underlie bile acid metabolism could revolutionize treatment options for liver cancer. By focusing on FXR activation and YAP inhibition, researchers are beginning to map out potential therapies that could stem the tide of liver disease progression. For example, enhancing FXR function may improve bile acid homeostasis and reduce the risk of liver injury, which is crucial in preventing hepatocellular carcinoma.
Furthermore, understanding the molecular dynamics involved in bile metabolism opens doors to innovative approaches that may incorporate genetic and genomic tools. As research continues, it is imperative to conduct clinical trials that assess the effectiveness of these new therapies, ensuring that they can provide tangible benefits to those affected by liver diseases. Treatments that can address both the symptoms and the cause of liver cancer will undoubtedly play a vital role in improving patient outcomes.
The Importance of Bile Acids in Metabolic Processes
Bile acids are not just digestive detergents; they are critical regulators of various metabolic pathways in the body. Their role in nutrient metabolism highlights their importance beyond fat digestion. The study by Yingzi Yang emphasizes that intact bile acid signaling is essential for maintaining metabolic homeostasis and preventing the onset of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. This discovery reiterates the significance of bile acids in overall health.
Moreover, the hormonal-like functions of bile acids extend into glucose and lipid metabolism, influencing liver health. A better understanding of how these metabolites interact with cell signaling pathways can improve treatment approaches for liver disease and other metabolic disorders. By focusing on the holistic roles of bile acids, researchers can develop more effective therapies that target related pathways, showcasing the interconnectedness of metabolic health and liver function.
Future Directions in Liver Disease Research
The advancements in understanding the mechanisms behind bile acid metabolism raise important questions regarding future liver disease research. Investigating molecular pathways such as YAP and FXR might reveal new therapeutic targets that can mitigate liver damage and prevent diseases like hepatocellular carcinoma. Ongoing research efforts strive to explore these pathways further, hoping to unlock novel treatment interventions.
Moreover, future studies should encompass a broader range of bile acid functions and their implications in liver disease. These insights could lead to discovering new biomarkers for early diagnosis and better-targeted therapies for liver cancer, improving patient survival rates and quality of life. As scientific exploration expands, it becomes evident that the liver’s role in systemic health is fundamental, necessitating continued focus in medical research.
The Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Liver Cancer
Understanding the pathophysiology of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, involves examining the roles of bile acids and signaling pathways. The study of YAP’s repression of FXR illuminates how disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to cancerous transformations in liver cells. Recognizing these fundamental processes is crucial for devising effective prevention and treatment strategies for liver cancer.
Research in this area should also consider the environmental and genetic factors that contribute to liver disease. Combining genomic studies with clinical findings may enhance our comprehension of liver cancer development, enabling researchers to create targeted interventions. Understanding the multifactorial nature of liver disease will facilitate holistic treatment approaches and improve patient outcomes in liver cancer.
The Link Between Liver Inflammation and Cancer Progression
Liver inflammation is a significant driver of hepatocellular carcinoma and is often a consequence of bile acid imbalance. Chronic liver inflammation leads to a microenvironment conducive to cancer development. The study by Yingzi Yang highlights how biliary dysfunction contributes to hepatic inflammation, accelerating the progression to liver cancer. Thus, addressing inflammation through regulatory pathways could be key to liver disease treatment.
Strategies aimed at reducing liver inflammation, such as anti-inflammatory therapies or lifestyle modifications, may offer additional protective effects against cancer development. Maintaining a healthy liver environment is crucial, and understanding how bile acids interact with inflammatory pathways can provide deeper insights into cancer prevention. Collaborative efforts in research are essential for expanding knowledge on this critical relationship.
The Role of Nutrition in Liver Health and Disease Prevention
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining liver health and preventing diseases like hepatocellular carcinoma. The composition of bile acids is influenced by dietary intake, highlighting the importance of a balanced diet rich in nutrients. Nutritional interventions that promote healthy bile acid production can significantly reduce the risk of liver disease. As discussed in recent studies, incorporating specific foods can help regulate bile acid composition and enhance liver function.
Conversely, nutritional imbalances can exacerbate bile acid dysregulation and contribute to inflammation and liver injury. Understanding the relationship between diet and bile acid metabolism provides an opportunity for developing preventive strategies against liver diseases. Empowering individuals with knowledge about liver-friendly dietary practices is crucial in the broader context of liver disease prevention and management.
Exploring Genetic Factors in Liver Disease Susceptibility
Genetic predispositions play a significant role in an individual’s susceptibility to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Research has revealed several genetic variants that may influence bile acid metabolism and liver health. Analyzing these genetic factors is essential for understanding how some individuals develop liver cancer more readily than others and could inform targeted prevention strategies.
As researchers continue to unravel the complex genetic landscape associated with liver disease, the potential for personalized medicine emerges. Identifying individuals at heightened risk for bile acid imbalances may enable more proactive monitoring and early intervention. Genetic studies combined with data on bile acid metabolism could revolutionize how we approach liver disease treatment and prevention, paving the way for tailored therapeutic solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does bile acid imbalance relate to liver cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma?
Bile acid imbalance plays a significant role in the development of liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. When bile acid metabolism is disrupted, it can lead to overproduction and accumulation of bile acids in the liver, causing liver injury, inflammation, and ultimately cancer. Addressing this imbalance may offer potential treatment pathways for liver cancer.
What role does YAP FXR signaling play in bile acid metabolism and liver disease?
YAP (Yes-associated protein) FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) signaling is crucial for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. In cases of bile acid imbalance, YAP can inhibit FXR’s function, disrupting bile acid metabolism. This interference leads to bile acid accumulation, which can contribute to liver inflammation and increase the risk of liver diseases, including cancer. Research suggests enhancing FXR function may provide therapeutic benefits.
What are the potential treatments for liver disease related to bile acid imbalance?
Potential treatments for liver disease linked to bile acid imbalance include strategies to enhance FXR function or promote bile acid excretion. By targeting the mechanisms of bile acid metabolism, such as inhibiting YAP’s repressive role, researchers are exploring pharmacological solutions that may reduce liver damage and slow the progression of liver cancer.
Can bile acid metabolism disruptions lead to liver injury or diseases?
Yes, disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to liver injury and contribute to the development of various liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. An imbalance in bile acids can cause inflammation and fibrotic changes in the liver, highlighting the importance of maintaining proper bile acid balance for liver health.
What recent discoveries have been made regarding bile acid metabolism and liver cancer treatment?
Recent studies have identified a key molecular switch that regulates bile acid metabolism and its link to liver cancer. Researchers found that YAP inhibits FXR, leading to bile acid accumulation and liver inflammation. These findings open up new avenues for liver cancer treatments by suggesting that targeting these metabolic pathways may help manage liver disease more effectively.
How can enhancing FXR function benefit individuals with bile acid imbalance?
Enhancing FXR function can benefit individuals with bile acid imbalance by restoring proper bile acid metabolism, reducing liver injury, and potentially slowing the progression of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Therapeutic agents aimed at stimulating FXR activity are being explored as promising treatments for liver-related conditions.
Why is understanding bile acid imbalance important in liver disease research?
Understanding bile acid imbalance is essential in liver disease research because it reveals critical mechanisms behind liver injury, inflammation, and cancer development. By deciphering how bile acids influence metabolic pathways, researchers can develop targeted therapies that improve liver health and reduce the burden of liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Acid Imbalance | A critical imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, including liver cancer. |
| Discovery | Researchers identified a key molecular switch that regulates bile acid production. |
| YAP Role | YAP promotes tumor formation and disrupts bile acid metabolism by paralyzing FXR. |
| FXR Function | FXR is essential for bile acid homeostasis and its dysfunction leads to liver inflammation. |
| Treatment Implications | Potential treatment strategies include enhancing FXR function to reduce liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Research Support | The research is supported by NIH and the National Cancer Institute. |
Summary
Bile acid imbalance is a critical factor in the development of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent research has unveiled the molecular mechanisms driving this condition, particularly highlighting the role of the YAP protein in bile acid metabolism. Understanding how bile acid imbalance leads to liver cancer is crucial for developing effective treatment interventions. Future therapeutic strategies may focus on restoring bile acid homeostasis, thus offering hope for individuals at risk of liver diseases.