Cancer risk claims are a hot topic, capturing attention across various platforms from social media to scholarly articles. Understanding these claims is crucial for anyone looking to make informed health choices, especially when evaluating cancer risks that can potentially impact daily lives. With the rise of misinformation, the need for accurate cancer prevention facts is more urgent than ever. At Harvard, researchers have developed valuable resources, including a cancer risk quiz to help users navigate these complex claims effectively. By leveraging insights from Harvard cancer research, individuals can better discern which cancer risk claims are credible, thereby leading to healthier lifestyle decisions.
When exploring the dangers associated with cancer, it’s essential to recognize the spectrum of misinformation and reliable data circulating today. Terms like “carcinogen exposure” and “cancer risk assessments” underscore the significance of understanding how various factors contribute to the likelihood of developing cancer. With which substances and behaviors are individuals most at risk? Utilizing tools developed by health experts can empower people to take proactive steps in cancer prevention. The increasing importance of addressing misconceptions around cancer risk emphasizes a collective effort in fostering a scientifically-informed community.
Understanding Cancer Risk Claims: What You Need to Know
In today’s media landscape, cancer risk claims abound, making it challenging for individuals to discern fact from fiction. Studies from organizations like the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health highlight the importance of evaluating such claims critically. It is essential to understand that not every idea circulating on social media or discussed among friends holds scientific validity. Research-backed resources like the Cancer FactFinder can provide reliable information but require users to approach claims with an inquisitive mindset.
To reliably ascertain cancer risk, individuals should be aware of the leading causes of cancer and scrutinize the validity of various claims. Factors such as smoking, obesity, and even certain dietary habits have been scientifically linked to increased cancer risk. By delving into resources from trusted institutions, one can better navigate through the conflicting information often presented in casual conversations or sensational articles.
Evaluating Cancer Risks: Tools and Resources
Evaluating cancer risks is an important step toward prevention and early detection. Tools like the Cancer FactFinder provide a platform for individuals to search for specific claims regarding cancer risks and exposure. This online resource is crucial for demystifying various topics, such as the effects of alcohol consumption or the role of diet in cancer prevention. Understanding how these elements contribute to cancer risk is vital in making informed lifestyle choices.
In addition to self-assessment tools, cancer risk quizzes available through reputable health organizations offer a structured way to evaluate personal behaviors and conditions that may increase cancer probability. Engaging with these resources empowers individuals to take preventive measures seriously, such as adjusting their diets, increasing physical activity, and reducing exposure to recognized carcinogens.
Cancer Prevention Facts: What Research Tells Us
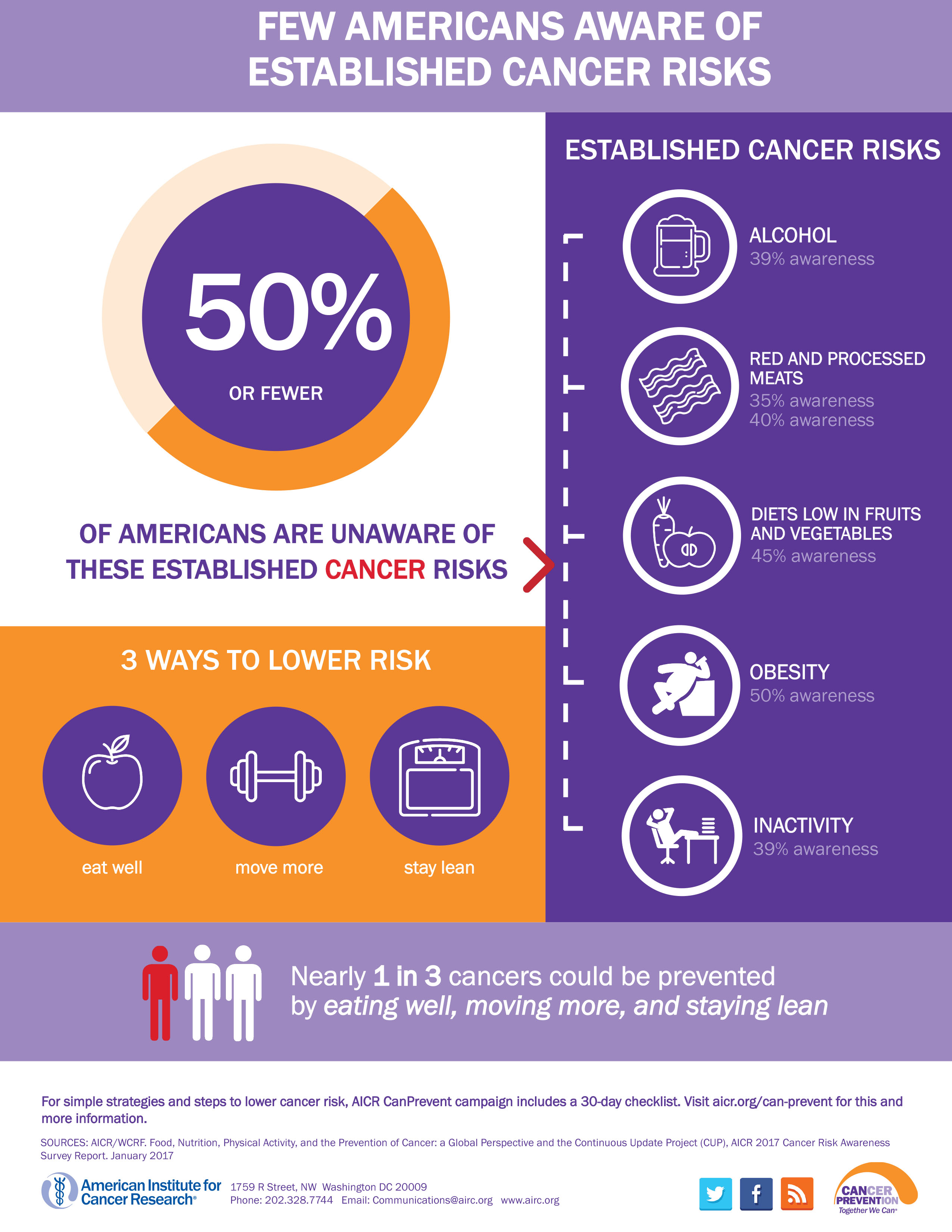
When it comes to cancer prevention facts, current research emphasizes the significance of lifestyle choices. Studies conducted by institutions like Harvard highlight that maintaining a healthy weight, being physically active, and consuming a balanced diet can considerably reduce cancer risk. For instance, research suggests that moderating alcohol consumption and limiting processed meat intake are pivotal in mitigating certain cancer risks.
Moreover, consistent scientific inquiries continue to reveal new insights into how specific foods and habits may support cancer prevention. Some evidence indicates that regular consumption of antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables could enhance the body’s defenses against cancer. Staying informed about ongoing research is paramount for those who wish to optimize their health and potentially lower their cancer risk.
Exploring the Cancer Risk Quiz: An Interactive Approach
The Cancer Risk Quiz is an interactive tool designed to engage individuals in understanding their potential cancer risk based on their lifestyle and habits. By answering a series of questions, users can gain insights into behaviors that may elevate their likelihood of developing cancer. This engaging approach is an excellent way for users to reflect on their choices and, if necessary, seek professional advice to mitigate risks.
Created in conjunction with experts at Harvard, the Cancer Risk Quiz also helps dispel myths that may surround cancer risk, encouraging users to delve deeper into scientifically supported facts. The quiz not only promotes awareness but serves as a gateway to additional educational resources, empowering individuals to lead healthier lives by making informed decisions.
Debunking Myths: Alcohol and Cancer Risk
Alcohol consumption remains a hot topic in discussions surrounding cancer risk. The U.S. Surgeon General has identified it as a leading preventable cause of cancer, linking heavy and regular drinking to various types of cancer such as breast and liver cancer. It’s crucial for individuals to recognize that even moderate alcohol intake can pose risks and to evaluate their consumption habits in light of these findings.
Furthermore, breaking these myths requires a cultural shift towards healthier alternatives and moderation. Educational initiatives from reputable sources, including Harvard research, aim to spread awareness about the potential dangers of alcohol on cancer risk. Such knowledge can empower individuals to make lifestyle changes that may reduce their cancer risk, underscoring the importance of informed decision-making regarding alcohol consumption.
Lifestyle Choices and Their Impact on Cancer Risk
Lifestyle choices significantly influence cancer risk, as evidenced by numerous studies. Factors such as diet, physical activity, and stress levels have consistently been linked to cancer predisposition. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and managing stress effectively are all vital preventive measures against cancer.
Moreover, understanding the interplay between these lifestyle choices and cancer risk is paramount. Research from institutions like Harvard encourages individuals to adopt comprehensive wellness strategies that encompass all aspects of health. By committing to a lifestyle that reduces exposure to known carcinogens and fosters overall well-being, one can take meaningful steps toward cancer prevention.
The Role of Sleep Patterns in Cancer Risk
Emerging research indicates that sleep patterns can significantly affect cancer risk. Disrupted sleep cycles have been linked to various health issues, including hormonal imbalances and weakened immune responses, which are critical factors in the body’s ability to ward off cancer. Acknowledging the importance of restorative sleep is essential for maintaining overall health and potentially reducing cancer susceptibility.
Individuals are encouraged to establish healthy sleep routines and prioritize quality sleep as a component of their preventive health strategy. By ensuring adequate rest, one can support bodily functions that combat cancer development. Awareness of the connection between sleep and overall health can further motivate individuals to make the necessary lifestyle adjustments to promote well-being.
The Impact of Diet on Cancer Risk: Exploring Food Choices
Diet plays a vital role in cancer risk, with research indicating that certain food choices can either promote or hinder cancer development. The consumption of processed foods, red meats, and sugary drinks has been linked to higher cancer risk, whereas diets rich in whole foods, healthy fats, and fiber are associated with reduced risk. Certain nutrients, like antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, may also provide protective benefits against cancer.
Engaging with resources that inform about healthy eating strategies can be a pivotal step toward lowering cancer risk. By making conscious dietary changes, individuals can significantly influence their health outcomes and foster long-lasting preventive habits, thereby contributing to a decline in cancer incidence.
Understanding the Connection Between Genetics and Cancer Risk
While lifestyle factors play a significant role in cancer risk, genetics also contribute to an individual’s likelihood of developing the disease. Certain inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, are well-documented risk factors for breast and ovarian cancers. Understanding family history is crucial for evaluating personal cancer risk, as it can guide proactive health measures and screening protocols.
Genetic counseling can play an essential role for those with significant family histories of cancer. This process provides valuable information about the potential implications of genetic testing and enhances individual awareness so that they can navigate their health journey with their unique risk profiles in mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are common cancer risk claims and how can I evaluate them?
Cancer risk claims are statements about what might increase or decrease the risk of developing cancer. To evaluate these claims accurately, the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health provides the Cancer FactFinder tool, which helps users assess the validity of various cancer prevention facts based on scientific research.
How does the Cancer FactFinder help with cancer risk claims?
The Cancer FactFinder is an online resource from Harvard that allows individuals to look up specific cancer risk claims. By checking these claims, users can determine whether they are supported or debunked by credible research, thus aiding in understanding cancer risks and prevention strategies.
Are alcohol consumption and cancer risk connected?
Yes, alcohol consumption is widely recognized as a leading preventable cause of cancer, according to the U.S. Surgeon General. Understanding the relationship between alcohol and cancer is crucial for evaluating cancer risks and making informed health choices.
Is there a cancer risk quiz available to learn more about cancer prevention facts?
Yes, the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health offers a cancer risk quiz designed to assess knowledge about cancer prevention facts. This interactive quiz helps users understand various factors that can influence cancer risk.
What lifestyle choices are linked to increased cancer risk?
Several lifestyle factors can elevate cancer risk, including low physical activity levels, obesity, and high stress. Awareness of these leading causes of cancer can help individuals make healthier lifestyle choices to mitigate their cancer risk.
Can consuming turmeric help reduce cancer risk?
While there is ongoing research into the effects of turmeric on cancer prevention, the consensus is that more research is needed to establish a clear link. Therefore, it’s essential to consult reliable sources or healthcare providers when evaluating such cancer risk claims.
Do pilots and flight attendants face higher cancer risks?
Research indicates that pilots and flight attendants may be at a higher risk for certain types of cancer. This is attributed to various factors including exposure to radiation and irregular sleep patterns, highlighting the importance of evaluating cancer risks in specific occupational groups.
How do sleep patterns affect cancer risk?
Disruptions in sleep patterns can hinder the body’s natural defenses against cancer. A consistent sleep schedule is essential for overall health, and understanding its connection to cancer risk is crucial for preventive health measures.
Is there a risk associated with using scented candles and cancer?
Yes, burning certain scented candles indoors could expose individuals to carcinogenic substances. It’s important to evaluate such cancer risk claims critically and consider safer alternatives for home fragrance.
What role does sunscreen play in reducing skin cancer risk?
Sunscreen is critical for protecting against skin cancer, regardless of skin type or weather. Misconceptions around sunscreen use can lead to increased cancer risk, emphasizing the need for accurate information on sun safety.
| Claim | True/False | Research Findings |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Surgeon General highlighted alcohol as a leading preventable cause of cancer. | True | Alcohol consumption is linked to several types of cancer. |
| Coffee consumption increases cancer risk. | False | Research suggests coffee may actually decrease cancer risk. |
| All types of mentioned meats are flagged as possibly carcinogenic. | True | Charred, processed, and red meats have been linked to cancer. |
| Burning scented candles can cause cancer-causing exposures. | True | Some candles release harmful chemicals when burned. |
| Pilots and flight attendants have a higher cancer risk. | True | Occupational exposure increases risk for these professions. |
| Turmeric helps in cancer prevention. | More research needed | Current evidence is inconclusive regarding turmeric’s benefits. |
| Using tampons raises cancer risk. | False | No research supports a link between tampons and cancer. |
| All lifestyle factors listed contribute to cancer risk. | True | Low activity, obesity, and stress are all linked to higher risk. |
| Disrupted sleep patterns hinder cancer defense. | True | Poor sleep can affect immunity and cancer defense mechanisms. |
| People with dark skin don’t need sunscreen. | False | Everyone, regardless of skin color, should use sunscreen. |
| Black men are at a higher risk for prostate cancer. | True | Statistics show higher rates of prostate cancer in Black men. |
Summary
Cancer risk claims are prevalent in today’s media landscape, leading to confusion about the genuine risks associated with cancer. The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health’s Cancer FactFinder serves as a valuable resource to debunk myths and clarify which cancer risk claims are supported by scientific research. By relying on reputable information, individuals can make informed choices to reduce their cancer risk.