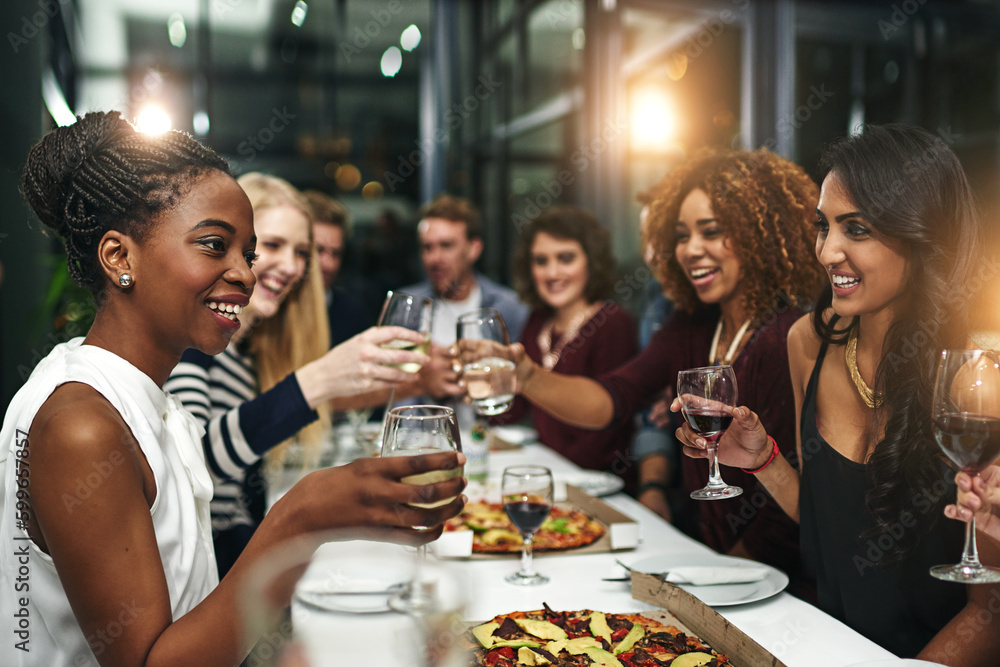
Dining with others and happiness intertwine in profound ways, shaping our experiences and emotional well-being. Research indicates that shared meals are not just rituals but pivotal happiness indicators that reinforce social connections. A study featured in the World Happiness Report highlights that individuals who enjoy meals with companions tend to express higher life satisfaction, paralleling traditional measures like income. Alarmingly, the American Time Use Survey reveals a growing trend of people opting to dine alone, with one in four Americans reported to have eaten all their meals alone in a single day. As we explore the impacts of meal sharing, it becomes evident that fostering connections through dining can enhance our happiness and overall quality of life.
The act of gathering around a table not only fulfills our nutritional needs but also nurtures our social relationships and emotional health. Studies suggest that such communal dining experiences can contribute significantly to individual well-being by enhancing bonds and providing a sense of belonging. As more people face social isolation, examining the different dimensions of meal sharing and its effects on mental wellness is increasingly valuable. Researchers emphasize that the quality of our social interactions, particularly during meals, could be a critical determinant of our happiness. As we delve into this topic, we uncover how fostering communal eating habits might serve as a vital strategy in promoting social connectivity and enhancing happiness.
The Connection Between Shared Meals and Happiness
Shared meals play a critical role in enhancing well-being by fostering social connections. When people gather around a table to eat, they engage in conversations that solidify relationships and build community. The phenomenon is supported by findings from the *World Happiness Report*, which shows that individuals who frequently dine with others report higher life satisfaction and express more positive emotions. This indicates that meal sharing is not merely an act of nourishment but an essential practice rooted in social bonding, contributing to overall happiness.
Furthermore, the benefits of sharing meals extend beyond just immediate social interactions; they pave the way for sustained emotional and psychological health. As highlighted in recent studies, including the *American Time Use Survey*, the decline of shared meals among Americans could correlate with rising feelings of loneliness and dissatisfaction. The evident decline in communal dining, especially among younger generations, raises concerns about social isolation and emphasizes the need for conscious efforts to return to shared meals as a vital practice for enhancing happiness.
Loneliness and the Decline of Shared Meals
In today’s society, there is a noticeable trend towards dining alone, with the *American Time Use Survey* reporting a striking increase in individuals eating alone. This shift may significantly impact mental health and community cohesion. The growing prevalence of solitary meals contributes to loneliness, thereby diminishing happiness indicators across various demographics. With many people reportedly skipping shared dining experiences, researchers are urging a reevaluation of lifestyle choices that promote social interactions and connections.
The implications of this trend are alarming, as shared meals provide a platform for emotional exchange and support, helping combat feelings of loneliness. Many people may not even realize how influential social connections are on their happiness levels. Studies suggest that incorporating regular shared meals into one’s routine could improve well-being and fortify social networks. If the trend of eating alone continues, we might be compromising not only our happiness but also the very fabric of our society.
The Importance of Dining Together for Emotional Well-being
Dining with others is often linked to enhanced emotional well-being. Sharing meals presents opportunities for conversation, laughter, and bonding, which are integral to maintaining personal relationships and social networks. As demonstrated by research analyzing trends in dining habits, those who prioritize shared meals generally report feeling happier and more fulfilled. The act of enjoying food together elevates mood and strengthens the emotional connections that help us thrive.
Moreover, societal attitudes towards meal sharing can influence individual behavior significantly. Encouraging communal eating can lead to healthier emotional states, more significant social support, and the development of meaningful connections. By recognizing the importance of shared meals, individuals and communities can foster environments that promote happiness and resilience through collective dining experiences.
Investigating the Causal Links Between Shared Meals and Happiness
The relationship between shared meals and happiness has sparked considerable interest in the research community, leading to questions about causality. Does sharing meals make people happier, or do happier people tend to share meals more often? While definitive causative relationships need deeper investigation, the evidence suggests a strong correlation worth studying further. Understanding how meal sharing relates to happiness could provide insight into effective interventions designed to enhance well-being.
Future research aimed at addressing these causative dynamics could reveal essential insights into how social practices, like shared dining, significantly impact mental health. As policymakers and psychologists seek solutions to combat social isolation and enhance well-being, recognizing the dynamic relationship between shared meals and happiness becomes crucial. The potential for interventions aimed at increasing communal dining experiences could play a transformative role in enhancing both individual and community happiness.
Promoting Shared Meals as a Strategy for Improved Well-Being
Given the correlation between shared meals and happiness, it is vital for communities to promote dining together as a strategy to improve overall well-being. Initiatives that encourage family dinners, communal lunches, or community-centered meal events could alleviate feelings of isolation and boost happiness. As research indicates, the act of sharing food is an ancient practice that brings people together, and revitalizing this tradition can lead to healthier communities.
Local governments and organizations can implement programs aimed at increasing opportunities for shared meals, whether through public events or community kitchens. These efforts not only foster social connections and emotional health but also help in bridging cultural divides and promoting inclusivity. In doing so, communities can create environments where shared meals flourish, setting the stage for collective happiness and enriched social bonds.
Examining Meal Sharing Across Cultures
Meal sharing is a universal practice that varies across cultures, with each society bringing its unique traditions and significance to communal dining. In many cultures, shared meals symbolize unity and a sense of belonging, transcending age, gender, and socioeconomic factors. The rituals surrounding meal sharing in various countries highlight the cultural importance of dining together as an avenue for connection and happiness.
By exploring how different cultures embrace communal meals, we can appreciate the diverse ways in which social connections are fostered around food. Such studies not only underscore the significance of social interactions in enhancing happiness but also open up avenues for cross-cultural exchanges that can enrich personal experiences in dining. Promoting an appreciation for diverse meal sharing practices can help bridge gaps between communities, fostering mutual understanding and enhancing collective happiness.
Shared Meals: A Reflection of Social Connections
Shared meals reflect the strength and depth of social connections in our lives. When individuals gather around a table, it acts as a physical representation of community and solidarity, reinforcing bonds that contribute to emotional well-being. The act of sharing food allows for meaningful conversations and connections that nourish not just the body but also the spirit, enhancing happiness and creating lasting memories.
Research shows that individuals who maintain close social connections often report higher levels of happiness. This correlation indicates that nurturing these bonds through shared meals may serve as a proactive strategy to enhance well-being. As we prioritize cultivating social networks, understanding how shared meals contribute to these relationships can help enhance the quality of life for individuals and communities alike.
Future Research Directions on Meal Sharing and Happiness
The field of happiness research is continually evolving, highlighting the need for further exploration into the dynamics of meal sharing and its effects on well-being. Future studies could focus on identifying specific elements within meal-sharing experiences that contribute to happiness, such as the frequency of shared meals, the quality of interactions during dining, or the emotional context of these gatherings. Investigating these dimensions may provide deeper insights into how dining with others impacts both individual and collective well-being.
Additionally, there is a need for interdisciplinary approaches that incorporate psychology, sociology, and public health to create comprehensive frameworks around meal sharing. By harnessing diverse methodologies, researchers can develop nuanced understanding and effective policies aimed at promoting communal dining experiences. Ultimately, recognizing the significance of shared meals as a vital aspect of social life can lead to more informed strategies that benefit public health and individual happiness.
Reinforcing the Value of Shared Meals in Modern Society
In a world where technology often isolates individuals, reinforcing the value of shared meals is essential for nurturing human connections. Understanding that shared dining is a predictor of happiness provides a powerful argument for encouraging communal eating practices. By fostering environments that highlight the importance of sharing meals, we can combat the trend of dining alone and enhance social interaction, leading to stronger communities.
Moreover, promoting communal meals can serve as a mediator for addressing broader societal issues such as mental health and loneliness. Encouragement from family, friends, and institutions to prioritize shared meals can inspire positive cultural shifts towards dining practices. A reconnection to the tradition of shared meals could redefine social practices in contemporary society, emphasizing the joy and fulfillment that come from eating together.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does dining with others influence happiness indicators?
Dining with others significantly influences happiness indicators. Studies show that shared meals are associated with greater life satisfaction and the expression of positive emotions. People who regularly participate in meal sharing tend to report higher happiness levels, highlighting the importance of social connections in fostering well-being.
Is shared meals a more reliable indicator of happiness than income?
Yes, research suggests that shared meals may be a more reliable indicator of happiness than income. The World Happiness Report indicates that the frequency of shared meals correlates strongly with life satisfaction across various demographics, suggesting that social connections through dining are crucial for enhancing happiness.
What trends have been observed in dining habits based on the American Time Use Survey?
According to the American Time Use Survey, there has been a concerning trend where Americans are dining alone more frequently. In 2023, 1 in 4 Americans reported eating all of their meals alone the previous day, an increase of 53% since 2003. This trend negatively impacts potential happiness derived from meal sharing.
Can meal sharing directly cause an increase in happiness?
While studies show a strong correlation between meal sharing and happiness, it remains uncertain whether sharing meals directly causes happiness or if happier individuals tend to share more meals. Future research aims to clarify these dynamics and understand better the relationship between social dining and overall well-being.
What role do social connections play in meal sharing and happiness?
Social connections play a crucial role in meal sharing and enhancing happiness. Regularly dining with others strengthens bonds and alleviates feelings of isolation, contributing to better mental health and well-being. Encouraging shared meals can be a key area for fostering social connections in communities.
Why is it important to study the relationship between dining with others and happiness?
Studying the relationship between dining with others and happiness is vital as it could inform policy interventions aimed at improving mental health and reducing social isolation. Understanding how shared meals impact well-being can guide strategies to enhance social connections and community engagement, fostering overall societal happiness.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Shared Meals and Happiness | Dining with others is linked to higher life satisfaction and positive emotions. |
| Research Findings | Study shows meal sharing is predictive of happiness akin to income/employment status. |
| Trends in Dining Alone | Increase in Americans dining alone, with 1 in 4 reporting meals alone, up 53% since 2003. |
| Future Research Directions | Need for studies to determine whether sharing meals causes happiness or vice versa. |
| Importance of Social Connections | Shared meals can indicate well-being and serve as a basis for policy interventions. |
Summary
Dining with others and happiness are intricately connected, as sharing meals has been shown to enhance overall well-being more reliably than traditional metrics like income. The increasing trend of Americans dining alone highlights the challenge of fostering positive social connections that contribute to happiness. Encouraging shared meals among individuals could be a significant step towards improving mental health and building stronger communities, making it a valuable focus for future research and policy initiatives.