The ethical implications of CRISPR have ignited a critical dialogue in the realm of biomedical ethics, leading us to question the morality behind gene editing technologies. As advancements like sickle cell gene therapy emerge, the potential to cure debilitating diseases steps into a complex landscape fraught with ethical dilemmas. Proponents argue that CRISPR technology holds the promise of alleviating suffering, yet it simultaneously raises concerns regarding health justice and the possible repercussions of altering human genetics. By considering the implications of gene editing ethics, we confront questions about who decides which traits are worthy of modification. As we navigate these turbulent waters, it becomes imperative to strike a balance between scientific innovation and the ethical responsibilities it incurs.
The discourse surrounding CRISPR resonates deeply within the fields of genetic modification ethics and medical equity. With revolutionary advances such as the gene-editing capabilities of CRISPR, we find ourselves at the intersection of potential medical breakthroughs and profound ethical quandaries. This evolving technology provides unprecedented possibilities for treatments like sickle cell gene therapy, yet poses serious questions about fairness in healthcare access and the moral limits of human enhancement. By exploring these ethical concerns, we can better understand the implications of gene manipulation and how they intersect with broader societal issues. In doing so, we must be vigilant in ensuring that advancements are balanced with a commitment to health justice and the welfare of future generations.
Understanding CRISPR Technology
CRISPR technology, short for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, represents a groundbreaking advancement in gene editing. This technology allows scientists to make precise alterations to DNA, an ability that holds incredible promise for treating genetic disorders. By utilizing CRISPR, researchers can target specific genes associated with diseases, such as sickle cell anemia, and modify them at their source, potentially curing patients of hereditary conditions that previously had no viable solutions.
The implications of CRISPR technology extend far beyond simple gene corrections. It raises profound questions about the future of genetic manipulation in humans. As scientists explore the potentials of germline editing, where changes made would be passed on to future generations, we must consider the ethical ramifications. With the power to edit the human genome comes the responsibility to use this technology judiciously, ensuring it promotes health rather than exacerbates inequalities.
Frequently Asked Questions
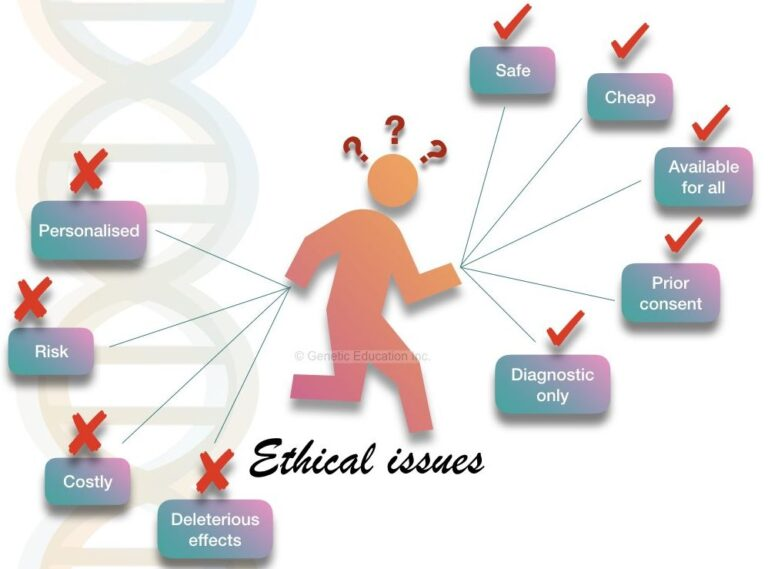
What are the ethical implications of CRISPR technology in gene editing?
The ethical implications of CRISPR technology in gene editing include questions about the morality of altering human genes, potential societal inequities, health justice concerns, and the repercussions of making genetic modifications. These considerations invite robust debate on who decides the acceptable uses of CRISPR, especially for conditions that do not impair life quality significantly, and the impacts on human diversity and rights.
How does CRISPR technology relate to health justice and equity?
CRISPR technology raises significant health justice issues as its high costs can exacerbate health inequalities. With treatments like sickle cell gene therapy priced at over $2 million, access becomes a major concern, particularly for marginalized communities. Addressing these disparities requires a careful ethical approach to ensure equitable access to the benefits of CRISPR gene editing.
What are the biomedical ethics considerations surrounding sickle cell gene therapy?
Biomedical ethics considerations surrounding sickle cell gene therapy focus on the potential for exploitation, consent, and the fairness of access to such transformative treatments. As therapies develop, ethical debates arise regarding who receives the benefits of CRISPR and how decisions are made about which genetic traits to modify or preserve.
What responsibilities do scientists have in addressing ethical questions in CRISPR gene editing?
Scientists carry a responsibility to engage with the ethical questions surrounding CRISPR gene editing by advocating for transparent decision-making processes and emphasizing the importance of public dialogue. They must consider the long-term implications of genetic interventions on individuals and society, balancing innovation with ethical standards.
How can society balance the promise of CRISPR with its ethical implications?
Balancing the promise of CRISPR with its ethical implications requires a multifaceted approach that includes public discourse, regulatory oversight, and interdisciplinary cooperation. Stakeholders, including scientists, ethicists, and policymakers, must work together to ensure that advances in CRISPR technology are leveraged to promote health equity and prevent misuse or unintended consequences.
What fears exist about the potential misuse of CRISPR technology in gene editing?
Fears surrounding the misuse of CRISPR technology include the potential for ‘designer babies,’ where genetic traits could be selected based on parental preferences, leading to ethical dilemmas about identity and diversity. Additionally, concerns about unregulated genetic modifications and their implications for bioengineering in areas like military applications amplify the urgency of regulating CRISPR technology.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Ethical Questions | Should we change human traits that are part of our identity? |
| CRISPR Technology Explained | CRISPR allows editing of somatic and germline genes, potentially curing diseases. |
| Cost and Access | The sickle cell cure costs around $2.2 million, raising equity concerns. |
| Health Justice | Innovation must consider health justice to prevent widening disparities. |
| Parental Rights | Should parents decide on the genetic attributes of their children? |
| Cultural Implications | Some view traits like deafness as human variation, not disorders. |
| Regulation Issues | Concerns over gene editing oversight in different countries. |
| Unintended Consequences | Editing genes may have complex and unforeseen effects. |
Summary
The ethical implications of CRISPR are profound and warrant careful consideration. As we have the capacity to alter human genetics, the question remains whether we should do so, especially concerning traits perceived as disabilities. Addressing health equity, oversight issues, and the potential for unforeseen consequences is crucial. CRISPR holds tremendous promise, yet it also brings a host of dilemmas that society must navigate thoughtfully to ensure that innovation benefits everyone, not just those who can afford it.