Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable discussion among health experts, mostly attributed to the growing concerns surrounding sugar cravings and their impact on our diets. As many processed foods are loaded with added sugars, understanding the effects of sugar on our brain and body becomes crucial for making healthy eating habits. While direct comparisons with substances like nicotine and alcohol can create confusion, the sugar addiction debate highlights the psychological pull of sweet foods and the potential for compulsive eating behaviors. This exploration into the nature of sugar leads us to assess not just its pleasurable qualities, but also the habits we form around consuming sugar-laden foods.
The topic of sugar’s potentially addictive nature is often presented through various lenses, including cravings for sweets and the role of processed foods in our diets. With an ever-increasing availability of sugary snacks, many individuals find their eating patterns influenced by these cravings. Furthermore, this examination delves into the psychological effects of indulging in sugary foods and the challenges of maintaining balanced nutrition amidst a culture that celebrates sweetness. Addressing these aspects can foster deeper conversations about how to develop healthier eating habits while still enjoying the flavors that sugar brings to our meals. Ultimately, understanding the complexities of our relationship with sugar is vital for promoting better overall health.
The Controversial Debate on Sugar Addiction
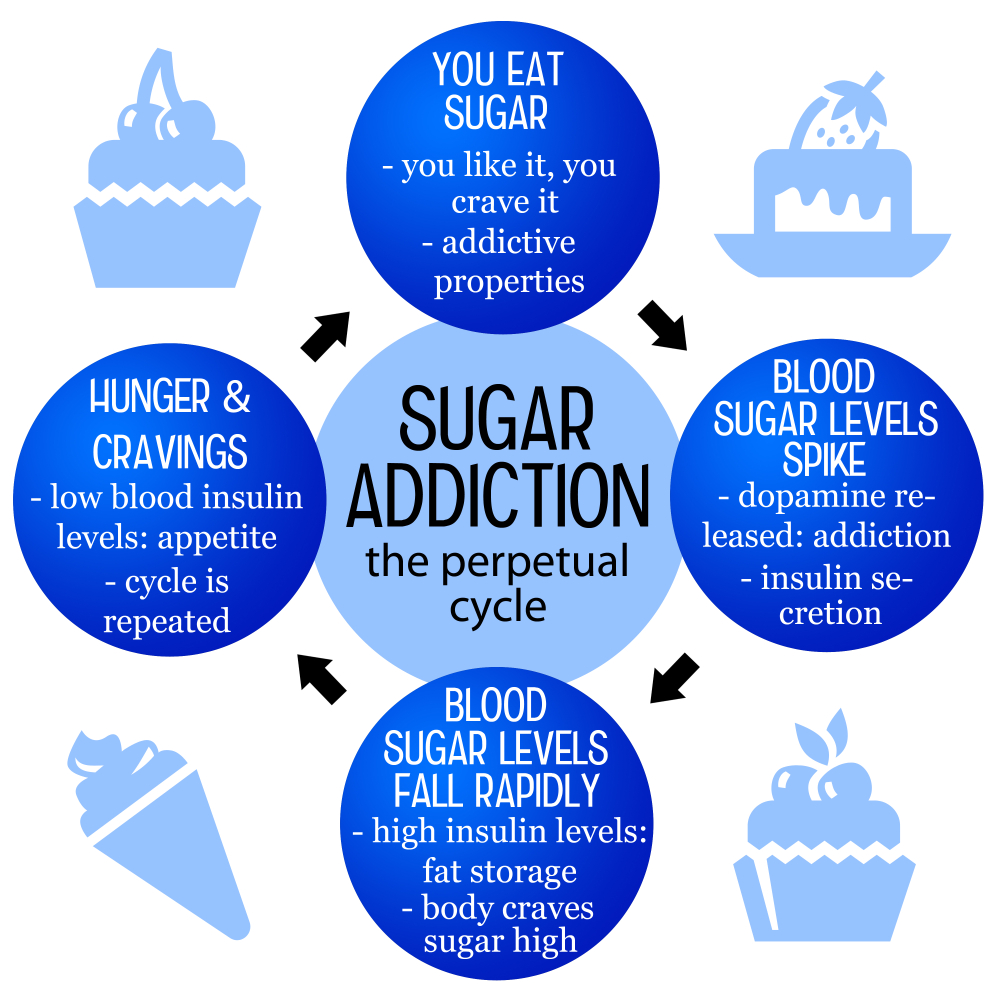
The question of whether sugar is addictive has sparked a great deal of debate in the scientific community, especially among nutritionists and psychologists. While substances like alcohol, nicotine, and opiates meet strict clinical criteria for addiction, sugar does not fall into the same category. However, the way sugar affects our brains can mirror aspects of addiction — particularly the intense cravings it can provoke. Many individuals experience compulsive eating behaviors related to sugar, suggesting a possible link to addiction-like symptoms. This phenomenon has led researchers to explore the effects of sugar on the brain’s reward pathways, to better understand the mechanisms at play.
In modern diets, sugar is ubiquitous, primarily found in processed foods that are designed to be highly palatable. This increases the likelihood of developing cravings for sugary items, which can lead to habitual consumption that resembles addictive behavior. Unlike addictive drugs or alcohol, though, sugar is a naturally occurring substance found in fruits and other healthy foods, indicating that the issue may not solely lie with sugar itself, but in its overconsumption through processed options. As scientists continue to investigate this sugar addiction debate, it’s clear that more awareness around dietary choices is necessary to foster healthier eating habits.
Understanding Sugar Cravings and Their Effects
Sugar cravings can be powerful and difficult to resist, often leading to feelings of guilt and frustration after indulgence. When we consume sugar, our bodies release dopamine, reinforcing the desire to seek out more sugary foods. This pleasurable response can make it challenging to moderate sugar intake, especially when under stress. The availability of processed foods, which typically contain high levels of added sugar, further exacerbates the situation. People may find themselves reaching for these convenient snacks and drinks, unaware of how their choices might impact their health.
Moreover, the effects of sugar on mood and energy levels are significant. After the initial energy boost from sugar, people may experience a crash that can lead to irritability and fatigue, creating a vicious cycle of cravings. This pattern of eating can negatively influence overall health, making it crucial to develop a balanced approach to sugar consumption. Adopting healthy eating habits that prioritize whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce sugar cravings naturally. Instead of relying on processed foods laden with added sugars, individuals can nourish their bodies and maintain more stable energy levels throughout the day.
Navigating the Challenges of Processed Foods
The prevalence of processed foods in our modern diet complicates the discussion around sugar intake and addiction. Many processed snacks and meals are designed to be hyperpalatable, often containing high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. These ingredients heighten cravings and increase the likelihood of overeating. In many cases, individuals are not aware of how much added sugar they are consuming on a daily basis, as it is frequently hidden in foods marketed as healthy. Reading food labels is crucial for nutrition awareness and can help people make informed choices about their sugar intake.
Additionally, the convenience of processed foods often leads to fast-paced eating habits, leaving little room for mindful consumption. People may find themselves eating sugary snacks out of habit rather than hunger, which further reinforces cravings. To combat this, introducing whole, minimally processed foods into the diet can facilitate greater control over sugar intake and promote healthier eating habits. Focusing on meal preparation and planning can reduce the temptation to reach for ready-to-eat processed products, thus improving overall nutritional quality and health outcomes.
The Psychological Impacts of Sugar Consumption
Beyond the physical effects, sugar consumption can have significant psychological implications. Many individuals associate sugary treats with comfort and reward, which can create a strong emotional connection to these foods. This connection can lead to emotional eating, where people turn to sugary foods in response to stress, anxiety, or sadness. Understanding these psychological triggers is essential for addressing compulsive eating behaviors and managing cravings effectively. By recognizing the emotional aspects of eating, individuals can better navigate their relationship with sugar.
On the flip side, the journey toward reducing sugar intake can also lead to improved mental clarity and mood stability. When individuals successfully manage their sugar consumption, they often report feeling more in control and capable of making healthier dietary choices. Creating a positive feedback loop where one’s physical health improves also enhances mental well-being can be a motivating factor. Implementing gradual changes to reduce sugar, rather than going cold turkey, can help individuals adapt without triggering withdrawal-like symptoms, paving the way for healthier lifestyle choices.
The Importance of Moderation in Sugar Intake
Moderation is crucial when it comes to sugar consumption. While sugar is a natural part of many wholesome foods—like fruits and dairy—it is the excessive intake of added sugars that poses a health risk. The average American consumes far more sugar than is recommended by health organizations, which can lead to a myriad of health concerns, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Following guidelines suggested by the American Heart Association, which recommend limiting added sugar intake to 9 teaspoons per day for men and 6 teaspoons for women, can play a vital role in promoting long-term health.
It’s not just about reducing sugar; it’s also about improving overall dietary patterns. Incorporating more whole foods into one’s diet can naturally decrease sugar cravings, as these foods provide essential nutrients and fiber that help maintain energy levels and reduce feelings of hunger. By focusing on balanced meals composed of whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables, individuals can cultivate healthier eating habits that satisfy both nutritional needs and taste preferences, making them less reliant on sugary snacks and drinks.
The Role of Education in Healthy Eating Habits
Education plays a critical role in cultivating healthy eating habits and making informed dietary choices. Understanding the effects of sugar on the body, as well as recognizing how to read and interpret food labels, empowers consumers to take charge of their nutrition. Educational initiatives aimed at improving food literacy can help individuals make healthier choices, leading to reduced sugar intake and better overall health outcomes. Schools, healthcare providers, and communities should prioritize food education to foster a culture of healthy eating.
Additionally, nutrition education that includes strategies for managing cravings and understanding the psychological components of eating can be particularly beneficial. By equipping individuals with knowledge about sugar addiction and its associated effects, they can become more mindful eaters. This approach encourages personal accountability and promotes long-lasting lifestyle changes. Ultimately, informed individuals are better positioned to make choices that align with their health goals, paving the way for improved physical and mental wellness.
Exploring Alternative Sweeteners
As awareness of the potential downsides of sugar consumption grows, many individuals are turning to alternative sweeteners as a means of satisfying their sweet tooth without the added calories and health risks. While options such as stevia, monk fruit, and erythritol are popular and can provide sweetness without the same metabolic impact as sugar, it’s essential to approach these alternatives with caution. Not all sweeteners are created equal; some may still trigger cravings for sugary foods, which can undermine efforts to reduce sugar intake over the long term.
Consumers should integrate these alternatives into their diets mindfully. It’s beneficial to focus on whole foods that naturally contain sweetness, rather than solely relying on artificial or processed sweeteners. By reducing overall sweetness in the diet, individuals can recalibrate their taste buds and lessen the desire for intensely sweet flavors. This shift can be gradual, allowing the body to adapt effectively. Ultimately, the goal is to prioritize wholesome ingredients and enjoy sweets in moderation, ensuring that sugar remains a pleasurable part of life without becoming a source of addiction.
The Link Between Sugar and Chronic Health Issues
Excessive sugar intake has been linked to a range of chronic health conditions, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and even certain cancers. The high caloric content of sugary foods and drinks, combined with their lack of nutritional value, makes them a significant contributor to weight gain and related health issues. Reducing sugar consumption is a pivotal step in preventing these conditions, which is why understanding the importance of monitoring sugar intake is essential for individuals looking to improve their health.
Furthermore, the inflammation caused by high sugar diets can exacerbate chronic illnesses and lead to a cycle of health complications. For instance, insulin resistance, a key factor in type 2 diabetes, can be intensified by a diet high in added sugars. Making conscious choices to limit sugar and prioritize nutrient-dense foods can mitigate these risks. By adopting healthier eating habits and advocating for lower sugar in public health discussions, communities can work towards healthier populations and a reduction in the prevalence of sugar-related chronic diseases.
Creating a Balanced Diet: Practical Tips
Creating a balanced diet that minimizes sugar intake requires practical strategies and intentional planning. It is essential to prioritize whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, which are not only nutritious but can also help stave off cravings. Planning meals in advance and preparing snacks that are low in added sugars can assist in managing cravings and maintaining steady energy levels. By keeping a well-stocked kitchen with healthy options, individuals can resist the temptation of sugary convenience foods, fostering a healthier lifestyle.
Additionally, incorporating mindful eating practices can greatly aid in managing sugar cravings and improving dietary habits. This includes savoring each bite, eating without distractions, and paying attention to hunger cues. By fostering a more mindful relationship with food, individuals can enhance their overall eating experience and make healthier choices that align with their well-being goals. Gradually replacing sugary snacks with fruit, yogurt, or nuts can also help establish sustainable habits that lead to long-term health benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
The sugar addiction debate often compares sugar to addictive substances like alcohol and nicotine, but while sugar can increase cravings and lead to compulsive eating, it is not classified as an addictive substance by clinical standards. Unlike drugs, sugar is a part of essential foods we consume for our health.
What are the psychological effects of sugar cravings?
Sugar cravings can lead to psychological effects similar to those experienced with food addiction. When consumed in excess, sugar may cause withdrawal-like symptoms such as anxiety and headaches upon cessation. Understanding the effects of sugar is crucial for fostering healthy eating habits.
How do processed foods contribute to sugar addiction?
Processed foods, which often contain high levels of added sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, contribute significantly to sugar cravings. These ingredients make foods more palatable and can lead to habitual consumption, ultimately making it hard to cut back on sugar.
Can reducing sugar intake improve healthy eating habits?
Yes, gradually reducing added sugar intake can enhance healthy eating habits. As individuals monitor their sugar consumption and opt for whole foods with natural sugars, they can curb cravings and improve overall nutrition.
What is the recommended daily limit for added sugar?
Health organizations recommend limiting added sugar intake to no more than 9 teaspoons per day for men and 6 teaspoons for women. Being mindful of the effects of sugar and adhering to these guidelines can help prevent health issues associated with excessive sugar consumption.
Why do people experience withdrawal-like symptoms after stopping sugar?
When individuals suddenly stop consuming sugar, especially from ultra-processed foods, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms due to the robust cravings established by habitual consumption. These symptoms can include headaches and anxiety, highlighting the challenge of breaking sugar habits.
Is it possible to enjoy sugar without becoming addicted?
Absolutely. It is essential to differentiate between healthy and unhealthy sugar consumption. Moderation is key; consuming natural sugars found in fruits and vegetables can enhance flavor and pleasure in our diets without leading to addiction.
What role does sugar play in a balanced diet?
Sugar, when consumed in moderation, can contribute to a balanced diet by enhancing flavors and providing energy. It is important to monitor and limit added sugars while ensuring that natural sources of sugar are included as part of a healthy eating habit.
How can I manage my sugar cravings effectively?
To manage sugar cravings, focus on balanced meals with whole foods, stay hydrated, and gradually reduce processed sugar consumption. Mindful eating and being aware of the psychological effects of sugar can also help in developing healthier eating habits.
Are there any long-term effects of high sugar consumption?
Consistent high sugar consumption can lead to numerous health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. It is important to be aware of the effects of sugar and monitor your daily intake to prevent such long-term complications.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of Addiction | Alcohol, nicotine, and opiates are classified as addictive based on strict clinical criteria, while sugar is not. |
| Cravings Related to Sugar | Sugar increases cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, but it is not classified as addictive. |
| Ultra-Processed Foods | These foods often contain added sugar and unhealthy ingredients, leading to cravings. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Stopping sugar can cause headaches, dizziness, and anxiety, but the severity is lower than for real drugs. |
| Moderation is Key | Sugar can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in low to moderate amounts. |
| Sugar Intake Recommendations | The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children. |
| Impact on Life | A suitable amount of sugar enhances flavor and enjoyment; complete elimination may be counterproductive. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The debate continues, as research suggests sugar does share some qualities with addictive substances, yet it does not meet the clinical definitions established for substances like alcohol and nicotine. While cravings for sugar can lead to compulsive behaviors due to the presence of ultra-processed foods, moderation is crucial. This means sugar can be enjoyed healthily when consumed in appropriate amounts. Understanding these nuances is important in managing sugar intake without categorizing it as a drug, as doing so may be misleading and counterproductive.