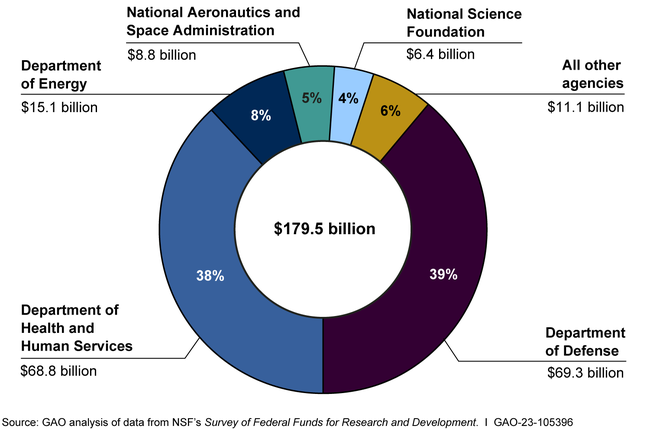
The U.S. innovation ecosystem is a cornerstone of global progress, with its dynamic interplay between public and private sectors fostering unprecedented advances in various fields, particularly biomedical research. This unique partnership has roots stretching back to World War II, where government-funded initiatives propelled breakthroughs like mass-produced penicillin, reshaping healthcare and military capability. Institutions like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) play a pivotal role in funding and supporting scientific research, ensuring a consistent flow of innovation. With a robust foundation built on collaborative efforts, the U.S. has established itself as a leader in technological advancement, continuously pushing the frontiers of knowledge. As the innovation landscape evolves, understanding its history, particularly through the lens of public-private partnerships, is essential to comprehend its current successes and future potential.
The American creativity framework, often hailed for its groundbreaking advancements, emerges from a rich tapestry woven through decades of collaboration between academics, industry, and government entities. This synergistic environment has been instrumental in enhancing sectors like health and technology, with foundational contributions from biomedical exploration and significant investments such as NIH funding. The intertwined relationship between federal support and private innovation has generated a thriving atmosphere conducive to scientific breakthroughs and cutting-edge developments. As we navigate through complex challenges, it is vital to recognize how the historical context of scientific research informs contemporary public-private partnerships in achieving substantial outcomes. The legacy of such collaborations not only highlights the successful trajectory of U.S. innovation but also sets the stage for future explorations in various scientific disciplines.
The Evolution of the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem
The U.S. innovation ecosystem has undergone remarkable evolution since its inception during World War II. Initially, the collaboration between the federal government and academic institutions was birthed out of necessity, as military leaders sought technological advancements to secure victories on the battlefield. This early partnership laid the groundwork for decades of technological advancement in the fields of biomedical research and public health. Today, this innovative collaboration continues to thrive and adapt, serving as a blueprint for other nations around the world.
Over the years, the synergy between government funding and academic research has led to groundbreaking discoveries, particularly in biomedical fields. The involvement of entities like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) transformed the landscape by directing resources to critical scientific inquiries. This shift not only enhanced the capacity for public-private partnerships but also ensured sustainable funding for long-term research initiatives. Such collaborative efforts have positioned the U.S. as a leader in biomedical innovations that have significantly impacted global health outcomes.
Historical Context of U.S. Biomedical Research
The story of U.S. biomedical research can be traced back to significant historical events, with World War II acting as a catalyst for innovation. As infectious diseases posed a grave threat to military personnel, the need for scientific research became paramount. This period marked a turning point where federal support for academic research became more systematic, resulting in strong public-private partnerships that leveraged resources effectively to address urgent health crises. The developments made during this era established a foundation for modern biomedical research practices.
One of the most notable achievements of this time was the mass production of penicillin, which revolutionized treatment approaches. The successful collaboration between government agencies, universities, and pharmaceutical companies demonstrated the potential of coordinated efforts in scientific research. The history of U.S. biomedical research is thus interwoven with wartime needs, and the resolve to combat disease has propelled the nation into a position of global leadership in scientific inquiry.
Public-Private Partnerships in Scientific Research
The concept of public-private partnerships (PPPs) has been central to the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in the realm of scientific research. These partnerships have allowed universities to engage in research that not only advances academic knowledge but also meets the practical needs of society. The benefits of such alliances are evident in myriad innovations, including new drug development, medical technologies, and treatment methodologies that have improved health outcomes across populations.
Moreover, the collaboration between the federal government and private sector entities enables the sharing of risks and rewards associated with scientific exploration. By pooling resources and expertise, these partnerships can address complex problems that no single entity could tackle alone. The narrative of U.S. biomedical research is rich with examples of how public-private alliances have led to transformative technologies, illustrating the critical role that these collaborations play in driving scientific progress.
Funding Challenges and Opportunities in Biomedical Research
As the U.S. innovation ecosystem faces new challenges, particularly regarding federal funding allocations, the future of biomedical research remains uncertain. Recent discussions surrounding the National Institutes of Health funding cuts have raised concerns about jeopardizing public-private partnerships that have proven essential to the progress of scientific inquiry. Ensuring steady funding is crucial, especially when the competitive nature of biomedical research demands constant investment in innovation.
Yet, this challenge also presents an opportunity for stakeholders in the scientific community to engage in dialogue about funding structures. Researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders must work together to advocate for policies that reflect the importance of sustained investment in biomedical research. By fostering a collaborative environment, new financial models can emerge to support innovative research activities, ensuring that the U.S. remains at the forefront of global scientific advancement.
Technological Advances Fueled by War Efforts
It is intriguing how historical wartime efforts have catalyzed numerous technological advancements, particularly in biomedical fields. The urgency to solve health issues during conflicts led to breakthroughs that have lasting implications even in peacetime. For instance, the research done by the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) during World War II not only addressed military needs but also spurred developments in pharmaceuticals and medical technologies that benefit civilians today.
These wartime innovations established a precedent for how government and academia could work together to solve pressing issues through scientific research. As military health problems were addressed through sophisticated research methodologies and innovations like antibiotics, the link between urgent demands and technological solutions became evident. These historical advancements underline the importance of institutional partnerships in achieving significant progress in biomedical research.
The Golden Age of Drug Development
The conclusion of World War II ushered in what many describe as a golden age of drug development, driven largely by the frameworks established during the conflict. The advancements made in medical research laid the groundwork for subsequent breakthroughs in treatment options for infectious diseases and beyond. The innovative practices that emerged from wartime collaboration served as a springboard for the thriving pharmaceutical industry we encounter today.
As researchers built upon the foundation set during the war, the principles of scientific rigor and collaboration took center stage in drug development processes. The U.S. innovation ecosystem became a beacon of hope, not only by developing lifesaving medications but also by cultivating a robust framework for scientific research that continues to evolve. Our ability to conduct cutting-edge biomedical research defines much of how U.S. contributions to global health challenges are perceived today.
The Impact of NIH on Biomedical Innovation
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) plays a critical role in sustaining the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in the biomedical sector. As one of the largest sources of funding for medical research worldwide, NIH’s support has been indispensable in fostering scientific discovery and innovation. The agency’s commitment to funding public-private initiatives has facilitated significant advancements in understanding diseases and developing new therapies.
The influence of NIH extends beyond mere financial backing; it also encompasses the establishment of rigorous research standards and ethical guidelines that shape how biomedical research is conducted. This oversight not only promotes public trust in scientific advancements but also encourages collaboration among academic institutions, government agencies, and private entities to pursue shared goals in health improvement. As a leader in funding scientific research, the NIH’s impact on global biomedical innovations cannot be overstated.
Training Future Generations of Scientists
In addition to facilitating research, the U.S. innovation ecosystem emphasizes the importance of training future generations of scientists. The investment in educational programs and initiatives within universities builds a skilled workforce capable of contributing to biomedical research and technological advancements. Engaging young researchers during critical periods, such as wartime or urgent public health issues, helps to develop a pool of talent that can drive future innovation.
Moreover, the collaborative nature of public and private partnerships creates opportunities for hands-on training, mentorship, and skill development for emerging scientists. These new generations are equipped to tackle complex health issues and contribute to the ongoing evolution of the U.S. biomedical landscape. As such, fostering an environment that encourages educational growth alongside research initiatives is pivotal for sustaining long-term success in scientific inquiry.
Preserving the Legacy of Biomedical Advancements
As we reflect on the historical context of the U.S. innovation ecosystem and its impact on biomedical research, it becomes evident how crucial it is to preserve the legacy of these advancements. Recognizing the collaborative efforts of various stakeholders—government, academia, and industry—highlights the importance of continued investment in research and development. Protecting the structures that have led to significant breakthroughs is vital for the ongoing progress in biomedical sciences.
Additionally, addressing current challenges in funding and operational efficiency is essential in maintaining the momentum of innovation. Through proactive measures that prioritize effective collaborations, the U.S. can ensure that its status as a global leader in biomedical innovation is not only preserved but also enhanced. The future success of this ecosystem depends on the collective dedication to nurturing research initiatives, fostering partnerships, and supporting the next wave of scientific inquiry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does NIH funding play in the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
NIH funding is a cornerstone of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in biomedical research. It provides essential financial support for academic institutions and researchers to advance scientific knowledge, leading to significant breakthroughs in health and medicine. By facilitating public-private partnerships, NIH funding helps bridge the gap between research findings and practical applications, driving technological advancement in the healthcare sector.
How did public-private partnerships contribute to the U.S. innovation ecosystem post-World War II?
Public-private partnerships have been vital to the U.S. innovation ecosystem, especially following World War II. These collaborations allowed the federal government to mobilize academic and corporate resources to address urgent technological needs. As a result, many advancements in biomedical research and other fields emerged, laying the foundation for the successful and dynamic U.S. innovation system we see today.
What is the historical significance of biomedical research within the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Biomedical research has played a crucial role in shaping the U.S. innovation ecosystem since World War II. The initial urgency for innovations in medicine during the war catalyzed advancements that transformed healthcare. As federal funding and public-private partnerships grew, the U.S. became a leader in biomedical technology, creating a rich landscape for ongoing scientific research and development.
How does the U.S. innovation ecosystem support technological advancement in biomedical science?
The U.S. innovation ecosystem supports technological advancement in biomedical science through a collaborative framework that involves government agencies, universities, and private industry. By leveraging NIH funding and fostering public-private partnerships, this ecosystem enables extensive research efforts that lead to new medical technologies and treatment solutions, further enhancing the health and well-being of society.
What challenges does the U.S. innovation ecosystem face regarding federal funding for scientific research?
The U.S. innovation ecosystem faces challenges related to federal funding, particularly in terms of budget cuts and policy changes that could restrict resources for biomedical research. Recent debates about NIH funding levels and indirect cost reimbursements demonstrate how changes in government support can impact public-private partnerships and, consequently, the overall health of the innovation ecosystem.
In what ways has the U.S. innovation ecosystem been emulated globally?
The U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in biomedical research, has been emulated globally due to its successful integration of federal funding, academic research, and industry collaboration. Countries around the world have looked to the U.S. model of leveraging public-private partnerships to stimulate technological advancements and drive economic growth, often attempting to replicate its successes in their own contexts.
What advancements in biomedical research can be attributed to the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Advancements in biomedical research attributable to the U.S. innovation ecosystem include the development of life-saving drugs, vaccines, and cutting-edge medical technologies. The collaboration fostered by NIH funding and public-private partnerships has led to breakthroughs such as the mass production of penicillin during World War II and more recent innovations like advanced gene therapies and personalized medicine.
How did World War II influence the development of the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
World War II significantly influenced the development of the U.S. innovation ecosystem by necessitating rapid technological advancements and fostering collaborations among government, academia, and private industry. The establishment of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) created a framework for public funding and support that initiated long-lasting relationships and research efforts that continue to benefit society today.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The U.S. innovation ecosystem is highly regarded globally, particularly in biomedicine. |
| Government-supported research began during World War II, leading to advancements like penicillin. |
| The partnership between federal government and academia has been crucial for technological advancements since 1940. |
| Federal funds have historically supported academic research and spurred private sector development. |
| The Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) was created during WWII to coordinate research efforts. |
| The successful development of penicillin exemplifies the effective collaboration between government and scientists. |
| This partnership has created a foundation for the ongoing success of U.S. biomedical innovation. |
| Young scientists trained during the war contributed significantly to the future of biomedical research. |
| Calls for efficiency and reforms in federal funding may risk undermining the success of the innovation ecosystem. |
Summary
The U.S. innovation ecosystem has proven to be a model for other nations, particularly in the field of biomedicine. Established during World War II, this system has evolved into a comprehensive partnership between the federal government, academic institutions, and the private sector. Through robust funding and collaboration, significant breakthroughs have been achieved, such as the mass production of penicillin, which saved countless lives during and after the war. Maintaining and fostering this innovative spirit is crucial for ongoing advancements in health and technology, ensuring that the U.S. remains at the forefront of global innovation.